A) further positive feedbacks.
B) further negative feedbacks.
C) a system that stays within certain limits.
D) a system exceeding positive or negative feedback limits.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following could be considered proxy data for measuring global warming EXCEPT
A) ice cores.
B) sea surface temperature.
C) tree ring.
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Urbanization
A) increases rainfall over the city center.
B) decreases temperature over the city center.
C) can raise or lower relative humidity.
D) reduces levels of smog, especially in the summer.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cooler water and stable atmospheric conditions bring dry "B" climate conditions to the
A) west coasts of southern hemisphere continents.
B) east coasts of southern hemisphere continents.
C) east coasts of northern hemisphere continents.
D) west coast of the Eurasian continent.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In comparing the distribution of acid rain and ozone pollution 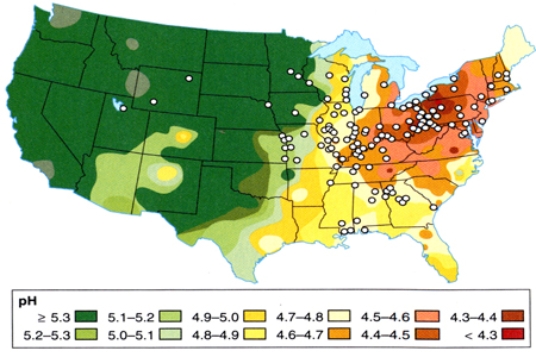
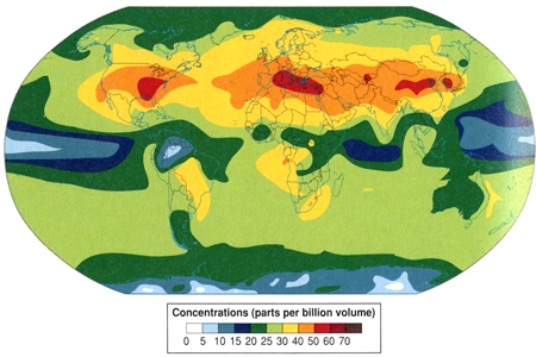
A) California suffers from the high levels of ozone pollution but not highest levels of acid rain.
B) the Gulf Coast suffers from the highest levels of ozone pollution and the highest levels of acid rain.
C) the East Coast has the lowest levels of ozone pollution and acid rain.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What line or region best corresponds with the location of "C" climates?
A) continental interiors, northern hemisphere
B) high latitudes
C) equator, high elevations
D) coastal locations, midlatitudes
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given that climate correlates closely with vegetation, what letter approximates the type of vegetation you would see for an Aw climate? 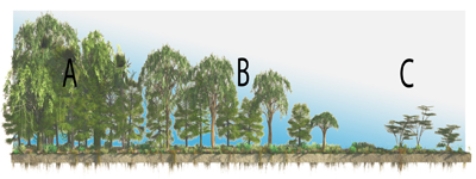
A) A
B) B
C) C
E) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a correct example of global warming creating a positive feedback
A) Ice has a higher albedo than water so replacing ice with water causes the surface to warm.
B) Ice has a lower albedo than water so replacing ice with water causes the surface to warm.
C) More water evaporating will create more low level clouds causing the surface to warm.
D) Less water evaporating will create more low level clouds causing the surface to warm.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would decrease the severity of air pollution in Los Angeles?
A) off shore breezes
B) valley surrounded by mountains
C) on shore breezes
D) inversion conditions
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What line or region best corresponds with the location of "A" climates?
A) continental interiors
B) high latitudes
C) equator
D) west coasts of continents
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a correct example of global warming creating a positive feedback?
A) Warming air melts permafrost releasing methane, a natural absorber of potent greenhouse gases.
B) Less water evaporating will create more high level clouds causing the surface to warm.
C) Warming oceans release more water vapor, a potent greenhouse gas which absorbs longwave radiation, further increasing temperature.
D) Warming oceans release less water vapor, a potent greenhouse gas which absorbs longwave radiation, further increasing temperature.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What line or region best corresponds with the location of "D" climates?
A) continental interiors, northern hemisphere
B) high latitudes, southern hemisphere
C) equator, high elevations
D) coastal locations, southern hemisphere
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The SO2 emissions displayed in this map derive mainly from the 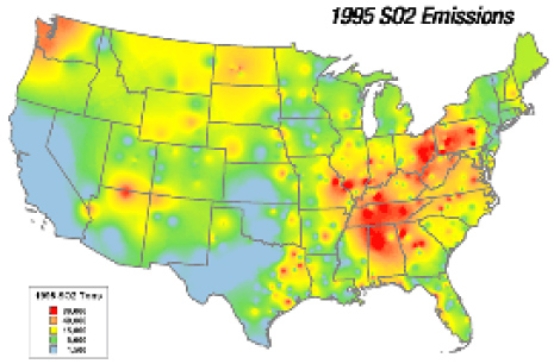
A) automobile emissions from point sources.
B) automobile emissions from non-point sources.
C) burning of coal from point sources.
D) burning of coal from non-point sources.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Atmospheric temperatures are influenced by all of the following greenhouse gases EXCEPT
A) nitrogen.
B) water vapor.
C) methane.
D) nitrous oxides.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would NOT be true regarding the urban heat island?
A) changes in albedo
B) retention of rain water
C) nighttime retention of longwave radiation
D) high concentration of waste heat from industry
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The seasonality of precipitation for the Humid Continental climate in North America can best be explained by
A) the moist eastern side of the subtropical high.
B) the moist western side of the subtropical high.
C) monsoonal precipitation.
D) westerly migration of mid-latitude cyclones.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Both sea surface (below) and air temperature (above) show a warming period beginning in 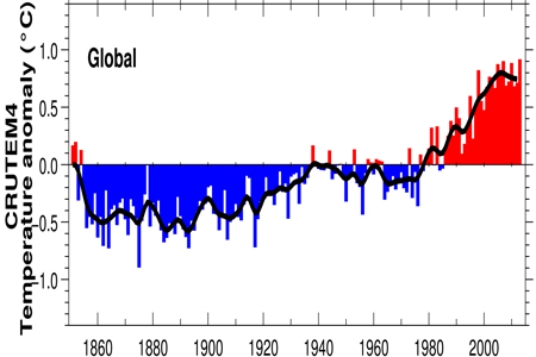
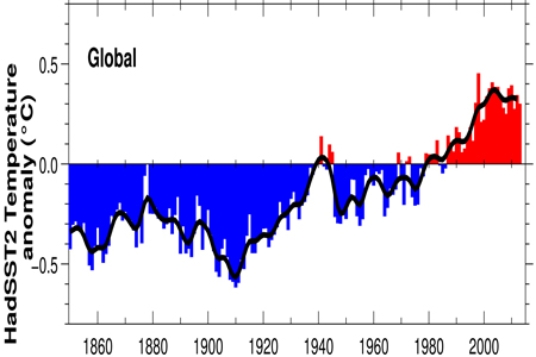
A) 1860.
B) 1940.
C) 1980.
D) 2010.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In classifying the climate of this imaginary country, the hottest and driest areas are in the 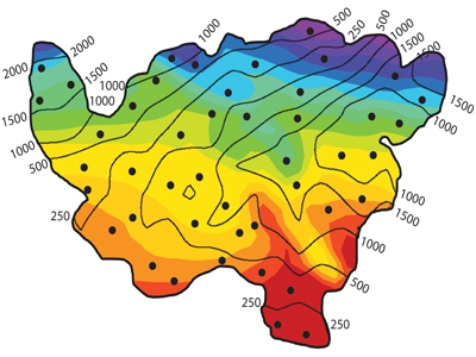
A) northeast.
B) southeast.
C) southwest.
D) northwest.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Imagine you fly a direct route from northern Greenland to the southern part of Hudson Bay.The correct sequence of climate types you would pass would be
A) Dfc, ET, E
B) Dfc, E, ET.
C) ET, E, Dfc.
D) E, ET, Dfc.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ozone pollution would be most favored in
A) sunny climates in summer when coal is burned in order to generate electric power.
B) sunny climates in winter when coal is burned in order to generate electric power.
C) sunny climates during the summer when volatile organic compounds can react with NO.
D) sunny climates during the winter when volatile organic compounds can react with NO.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 74
Related Exams