A) No. Large masses can have low luminosities and vice versa.
B) Yes. Mass and luminosity are related linearly: A star twice as massive has twice the luminosity.
C) Yes. The mass and luminosity are related, but not linearly: A star twice as massive has more than twice the luminosity.
D) Yes, but surprisingly there is an anticorrelation: Larger masses have smaller luminosities.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these statements is NOT true about the center of mass of a binary star system?
A) The center of mass is always on the line joining the two stars.
B) The center of mass is simultaneously a focus of the ellipse of each star's motion.
C) The center of mass is always more distant from the more massive star.
D) The center of mass can move with respect to the more distant background stars.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The spectral luminosity class of the star Spica is B1 V, and that of the star Ceti is G8 V. From this information, one knows that Ceti is _____ Spica.
A) cooler but has the same luminosity as
B) cooler and has a lower luminosity than
C) hotter but has the same luminosity as
D) hotter and has a lower luminosity than
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared with a star in the middle of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, a star in the upper right of the diagram is
A) fainter.
B) hotter.
C) larger.
D) nonexistent because there are no stars that appear in the upper right of the diagram.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Sun's absolute magnitude is about +5. The brightest stars in the sky have absolute magnitudes of about -10. What is the luminosity of these stars compared with that of the Sun, assuming that they have similar spectral light distributions?
A) 1 million times less
B) 5 times less
C) 1 million times greater
D) 15 times greater
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How can astronomers tell that some stars are relatively close to Earth?
A) The stars appear to move periodically back and forth against the background stars because of Earth's movement around the Sun.
B) The stars appear to be extremely bright and must therefore be very close to Earth.
C) The stars are occasionally occulted or eclipsed by the Moon; hence they must be close.
D) The light from these stars shows only a very small redshift caused by the universal expansion of the universe, so they must be close.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An astronomer is measuring the brightness of a particular star through a telescope, using different filters in the visual (yellow-green) , violet, and ultraviolet regions. What is the name of the technique being used by this astronomer?
A) spectroscopy
B) geometry
C) interferometry
D) photometry
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The star Hadar is classified as B1 II, which means that it is a
A) cool supergiant.
B) hot dwarf.
C) cool giant.
D) hot supergiant.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When observers look out at the night sky, the number of stars with
A) each magnitude (first, second, etc.) is about the same.
B) smaller magnitude numbers is much larger than the number of stars with larger magnitude numbers.
C) larger magnitude numbers is much larger than the number of stars with smaller magnitude numbers.
D) magnitudes around 3 is larger than either the number with magnitudes around 2 or the number with magnitudes around 4.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particular star has an absolute magnitude of +12 and a spectral class of A5. Using Figures 12-7 and 12-10 from the text, how would this star be classified? 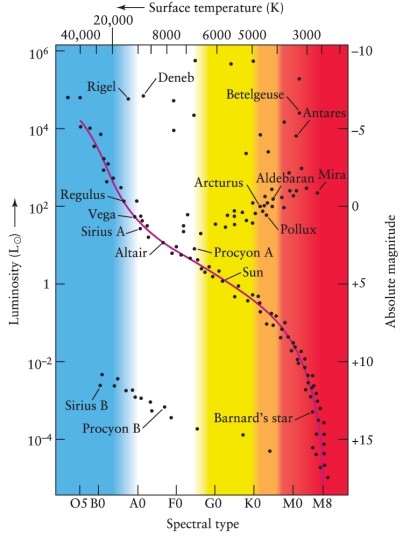
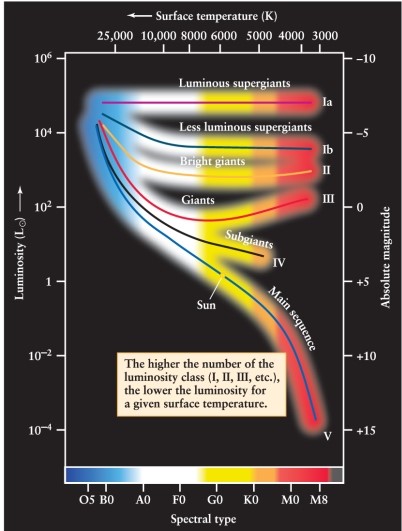
A) A5 I
B) A-type white dwarf
C) A5 V
D) A5 III
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The star Alphard has an apparent magnitude of 2.0, and the star Megrez has an apparent magnitude of 3.3. The only thing that can be said with certainty about Alphard is that it is _____ than Megrez.
A) brighter, as seen in Earth's sky
B) more luminous
C) fainter, as seen in Earth's sky
D) closer to Earth
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where are the MOST massive stars to be found in the main sequence of a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram?
A) upper left end
B) Main-sequence stars all have approximately the same mass, by definition.
C) center
D) lower right end
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these is not a type of true binary system, or, in other words, that the stars are NOT physically associated with each other?
A) optical double
B) visual binary
C) spectroscopic binary
D) eclipsing binary
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A typical white dwarf has a surface temperature about 4 times that of the Sun and a radius about 1 percent that of the Sun. What can one determine about the luminosity of a typical white dwarf from this information?
A) The white dwarf will be less luminous than the Sun.
B) The white dwarf and the Sun will have about the same luminosity.
C) The white dwarf will be more luminous than the Sun.
D) Nothing can be concluded about the relative luminosities from this information.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Apparent magnitude is a measure of a star's
A) intrinsic brightness (actual light output) .
B) size (diameter) .
C) temperature.
D) brightness, as seen from Earth.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the fundamental difference between absolute and apparent magnitude of a star?
A) The difference is +5 since absolute and apparent magnitude differ by this value by definition.
B) Apparent magnitude depends on the star's temperature, whereas absolute magnitude is independent of temperature.
C) Apparent magnitude depends on the size of the star, whereas absolute magnitude is independent of this parameter.
D) Absolute magnitude is an intrinsic property of the star, whereas apparent magnitude depends on its distance from Earth.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Among these spectral types, which signifies the hottest stellar surface temperature?
A) G
B) A
C) K
D) B
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As a person drives along a road, trees in the middle distance seem to shift in position relative to faraway hills. What name is given to this phenomenon?
A) parallax
B) perspective
C) Doppler effect
D) inverse-square law
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are the two physical parameters of stars that are plotted on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram?
A) mass and surface temperature
B) luminosity and mass
C) radius and mass
D) luminosity and surface temperature
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the surface temperature of a star is very low, which of these atomic or molecular constituents will produce the MOST prominent absorption lines in its spectrum?
A) Fe II
B) TiO
C) Mg II
D) He II
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 254
Related Exams