A) causes average total cost curves to be downward-sloping.
B) shifts average total cost curves downward.
C) offsets diseconomies of scale, making the average total cost curve flat.
D) is not important in the real world.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal rate of substitution of an isoquant curve is the rate at which:
A) inputs must be substituted for one another to keep costs constant.
B) inputs are substituted for output.
C) inputs must be substituted for one another to keep output constant.
D) the marginal productivity of a factor declines.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The upward-sloping part of the long-run average cost curve is explained by:
A) indivisible setup costs.
B) diseconomies of scale.
C) output levels that exceed the minimum efficient level of production.
D) decreasing marginal productivity.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Diseconomies of scale are associated with:
A) an upward-sloping long-run average cost curve.
B) an upward-sloping short-run average cost curve.
C) a downward-sloping long-run average cost curve.
D) a downward-sloping short-run average cost curve.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the graph shown. The output range in region b is associated with: 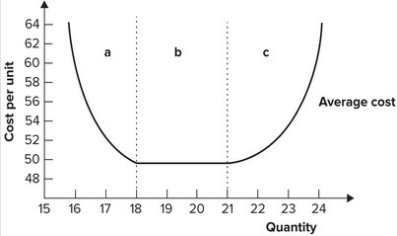
A) diminishing marginal productivity.
B) constant returns to scale.
C) economies of scale.
D) diseconomies of scale.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The upward-sloping portion of the short-run average total cost curve is caused by:
A) indivisible setup costs.
B) diseconomies of scale.
C) the absence of fixed inputs.
D) the presence of fixed inputs.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the text, globalization has led to greater U.S. specialization in:
A) marketing.
B) manufacturing.
C) farming.
D) manual labor.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a machine cost $50,000 initially and is expected to last for 20 years but is worth $60,000 after one year because it is in short supply, an accountant most likely would say that:
A) the machine's cost for each of its 20 years of existence is $2,500.
B) the machine's cost for each of its 20 years of existence is $3,000.
C) during the first year the machine had no cost; it provided a revenue to the firm.
D) the value of the machine will continue to increase 20 percent per year for the next 20 years.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economies of scale occur when a firm's long-run average total cost curve is:
A) upward-sloping.
B) vertical.
C) downward-sloping.
D) horizontal.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 129 of 129
Related Exams